- September 25, 2022
- Posted by: CFA Society India
- Category:BLOG, Events
Speaker: Ankur Gupta CFA, Vice President - Sustainable Investing, Northern Trust Asset Management
Moderated By: Sivananth Ramachandran CFA, CIPM, Director - Capital Markets Policy - India, CFA Institute
Contributed By: Swetha Rakhecha, CFA, Member, Public Awareness Committee, CFA Society India
Part 1: Intro to Climate Change
What is climate change?
Long term shift in temperatures and weather patterns caused by harmful gases emitted due to human activities
Looking at the economic risks and opportunities due to climate change:
Risks fall in two broad buckets
- Transition Risk: the risk to companies as they move to decarbonize. Will continue to rise before it stabilises. Encompasses environment as well as social impact.
- Physical Risk: physical damage to assets due to extreme weather events. Will continue to risk if no action is taken.
These risks need to carefully assessed while evaluating a company
Opportunities are wide and varied as we move to a low carbon economy:

A Bank of England research suggests that if no action is taken to mitigate climate change, the losses can range from $ 4 Trillion to upto $ 20 trillion
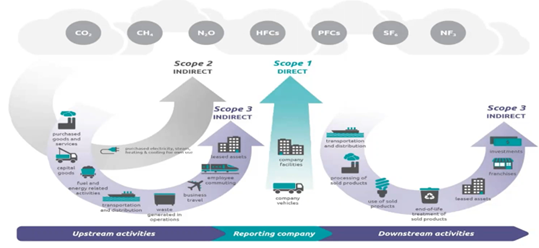
Counting GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions
Scope 1: direct emissions, directly coming from the activities of the company
Scope 2: indirect emissions – owned, purchased electricity
Scope 3: indirect emissions – not owned. Classified in 15 activities as either upstream and downstream.
Scope 1 and 2 are reported by 40% of the companies (19% for India), Scope 3 are reported by 25% (3% for India). As a result, majority of the carbon emissions are still estimated
Key Drivers shaping the future
- Global Regulatory Landscape is evolving (more regulation)
- Carbon Price Initiatives (emission allocation or carbon tax being adopted)
RCP 8.5% warming scenario: hypothetical, no action taken scenario where the world heats up by more than 4.9 Celsius. World GDP shrinks 17% by year 2100 (similar for India)
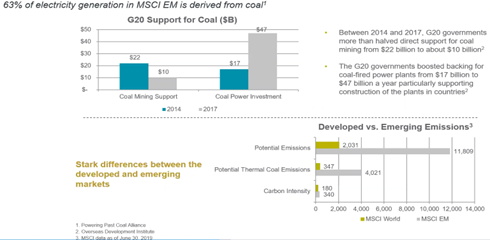
Emerging Markets should be a key focus for investment and development
Part 2: Approach to climate change integration
Data Quality and Data Validity are key concerns, as such Northern Trust has come up with industry first in house framework: NTAM ESG Vector

Step 1: Build a foundation of financial material ESG issues
SASB has identified that 72 out of 79 Sustainable Industry Classification System are significantly affected in some way from climate change
Step 2: Analyse and understand the effect of climate change at company level to assess the company valuation. 5 Key pillars
- Historical Carbon Trend
- Assess the Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 emissions
- What is the trend
- How is the company placed v the industry for carbon intensity
- Assessment of Transition Risk
- Recognise the transitions risks for the company
- Detailed reporting on transition risks and integration of these risks
- Managerial or board level responsibility for addressing transition risks
- Governance, Strategy and Risk management processes in place to update the board
- Operational efficiency and building technology advantage
- Consider carbon price to evaluate present and future project
- Assessment of Physical Risk
- Undertake relevant research and materiality analysis
- Assessment of opportunities and Company Commitments
- Commitment to become carbon neutral
- Ratings from CDP Climate Change
- Focus on energy efficiency
- Investment in platform and supply chain
Spectrum of Climate Investing Approaches
No size fits alls..
Driven by client preference and fund house capabilities..
Examples:

Carbon and ESG Overview
- 10% of the companies contribute to over 80% of total carbon intensity
- 80% of all carbon emissions come from Energy, Materials and Utilities
However, overall we need to look at it from a holistic process. There is significant bias across regions and sectors.
Part 3: Climate Change Landscape – India v ROW
- At Glasgow, India set a target to be net zero by 2070
- Switch to 50% renewable energy by 2030
There is a lot of opportunity to disrupt and innovate
- Green hydrogen and Green Ammonia
- 125% increase in renewable energy investments last year
- 2nd largest market in Asia for new solar PV capacity
50% of the companies in India still do not have carbon targets. The current model predicts an increase of 6 degrees (Celscius) by 2050.
Conclusion
- Investors should integrate ESG in their investments process
- Range of investment solutions available
- Context of debate is changing from “whether” to “when” to “HOW”
